Otitis Externa and Otitis Media are the inflammations of the outer ear and middle ear respectively. Although they are both ear inflammations and have some symptoms in common, their contributing factors are totally different.
What is Otitis Externa? Causes, Symptoms & Risk Factors
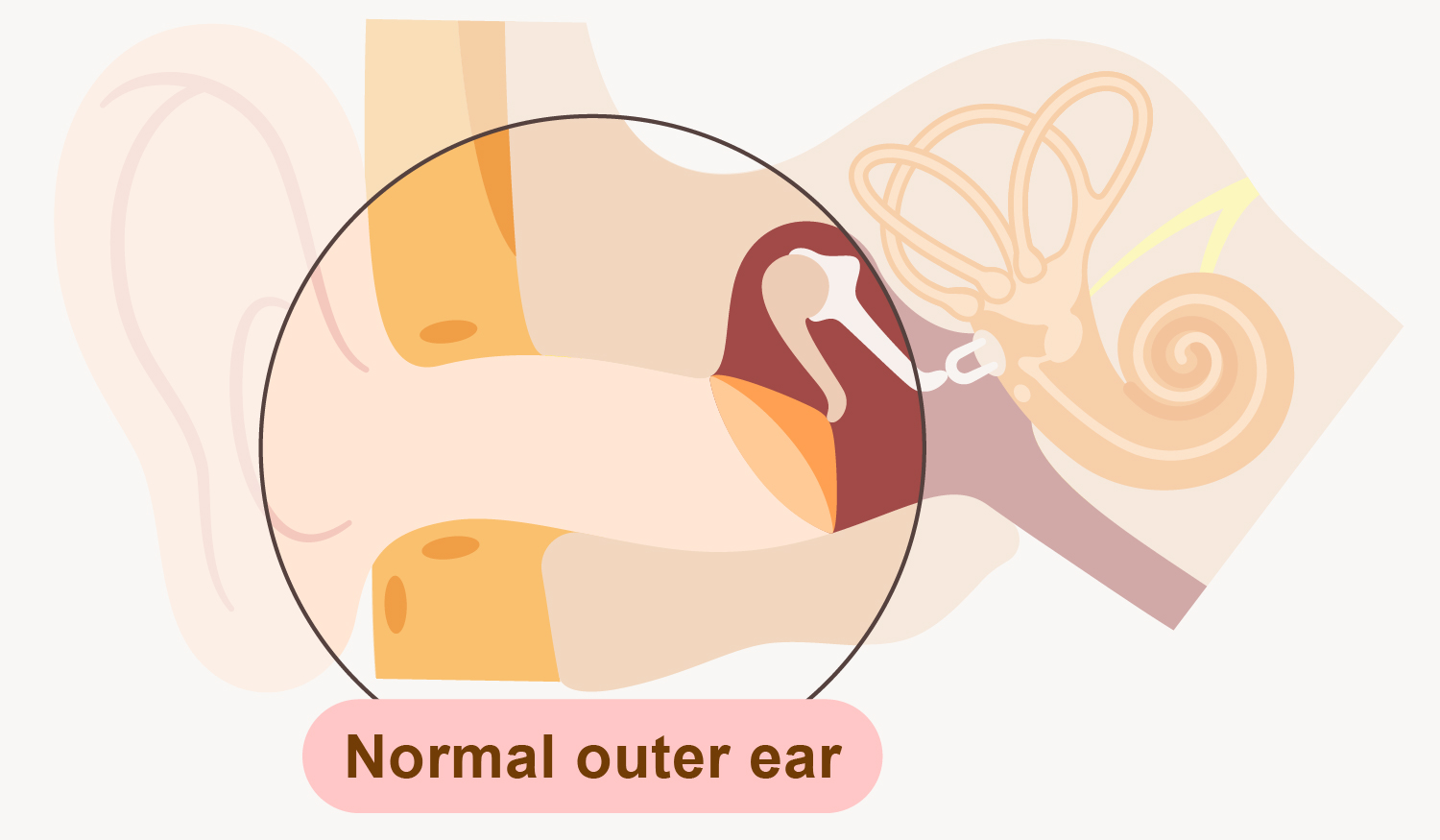
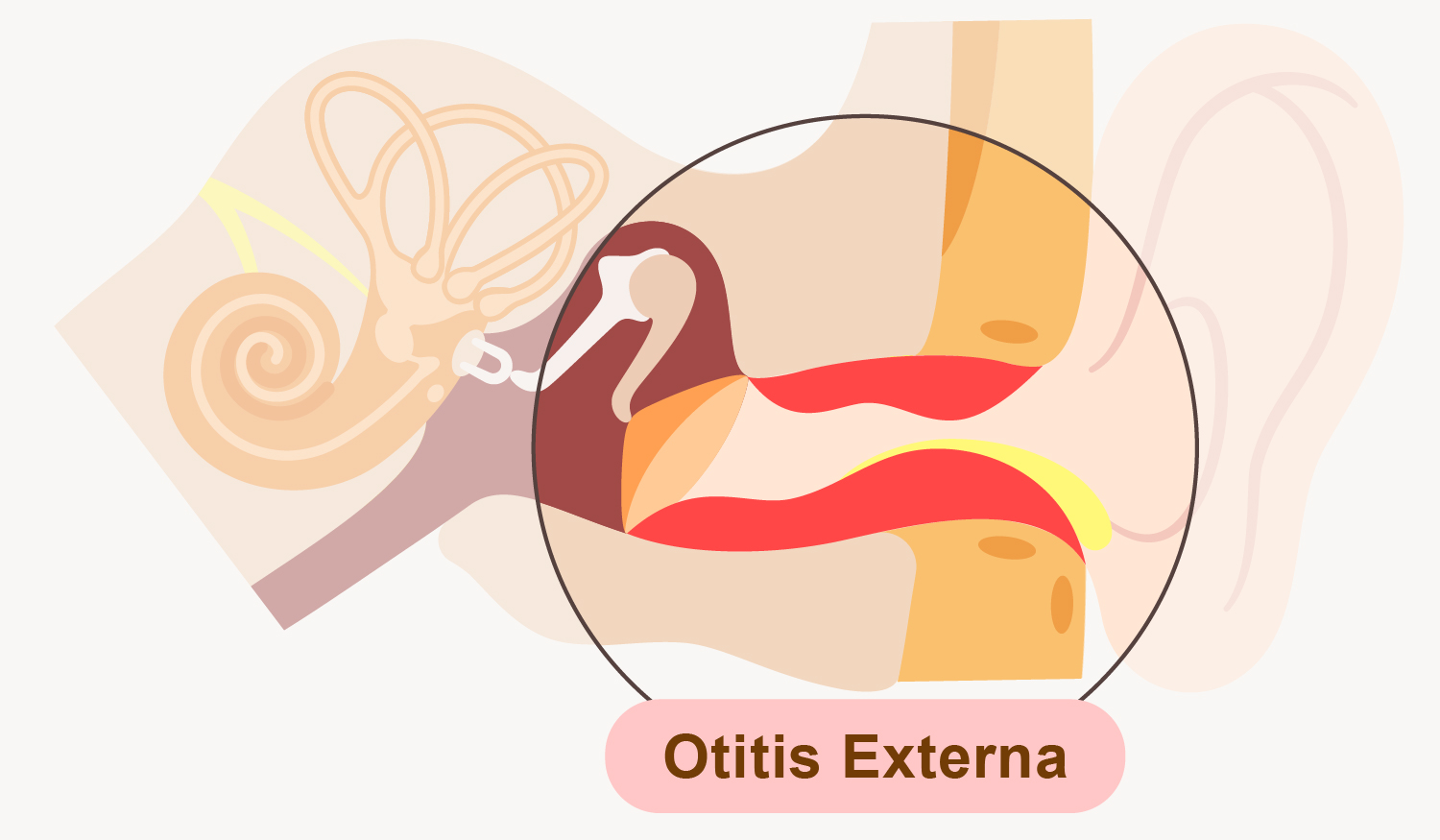
Otitis Externa, also named as swimmer's ear, is an inflammation or infection of the epidermis of ear canal which could cause by bacteria or fungi.
Symptoms of otitis externa include itching in ear, redness, burning sensation, pain (especially when touching or pressing the ear), feeling full or plugged in ear, muffled hearing or temporary hearing loss, drainage from the ear, swollen glands around the ear, fever and fatigue etc.
There are various risk factors contributing to otitis externa, which can be divided into two groups, they are individual factor and environmental factor. These two groups of risk factors would co-exist for otitis externa to happen.
The cause of Individual factor lies on why the epidermis of ear canal and its water-repellent layer lose its function as a protective barrier. This includes injury to the ear canal (i.e. scratching, trauma due to misapplication of cotton bud or foreign object, etc.) and dermatitis or other skin conditions in ear.
For the cause of environmental factor, it hinges on how the bacteria (or fungi) enters the ear canal, which includes using contaminated earpieces or earplugs, and in contact with contaminated water (i.e. shampoo wastewater, pool water and sea water, etc.).
Severity Levels and Treatment of Otitis Externa
Otitis externa can be classified as mild, moderate and severe levels. Patient with mild otitis externa will recover from the illness without treatment few days after symptoms appear; while patient with moderate otitis externa will suffer from the symptoms for extra days without any sign of recovery. At this moment, patient should seek medical advice from ENT specialist early. He will advise appropriate treatment for patient depending on the severity of the disease.
For patient with mild otitis externa, ENT specialist may prescribe medications for relieving the symptoms and suppressing the growth of bacteria (or fungi) in the ear canal. For more severe or complicated cases (e.g. earwax blockage induced otitis externa), specialist may firstly arrange ear toileting for patient, follow by prescribing medications for treatment. In general, patient will recover from moderate otitis externa in 7-10 days after medications kick in.
Patients who suffer from severe otitis externa are more likely to be the immunosuppressed group, such as elderly, people with diabetes, or patient who undergoes radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
The symptoms of severe otitis externa are similar to the mild and moderate otitis externa, but it lasts for an extended period of time, usually a month or above. When severe otitis externa is left untreated, it may trigger granulation tissue growing in the ear canal, or Bell's Palsy due to infection spread to the facial nerve.
Since most of the patients with severe otitis externa may suffer serious relapses, ENT specialist will usually admit the patient for close observation, and provide treatment with a course of antibiotics and ear toileting. Surgical debridement (means removing infected and dead tissue) may apply to patient with severe ear infection in order to prevent the spread of infection.
What is Otitis Media? Causes, Symptoms & Risk Factor
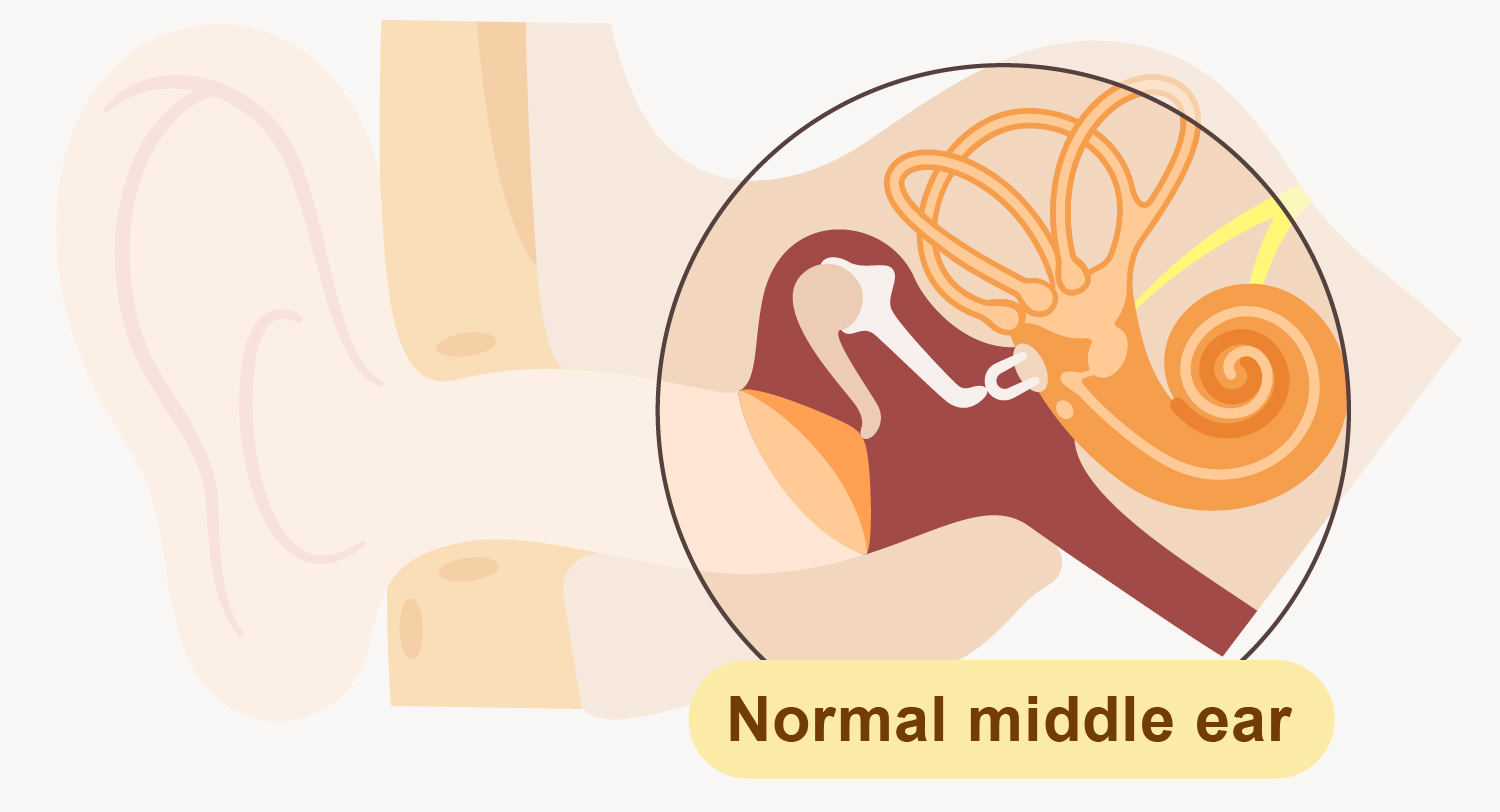
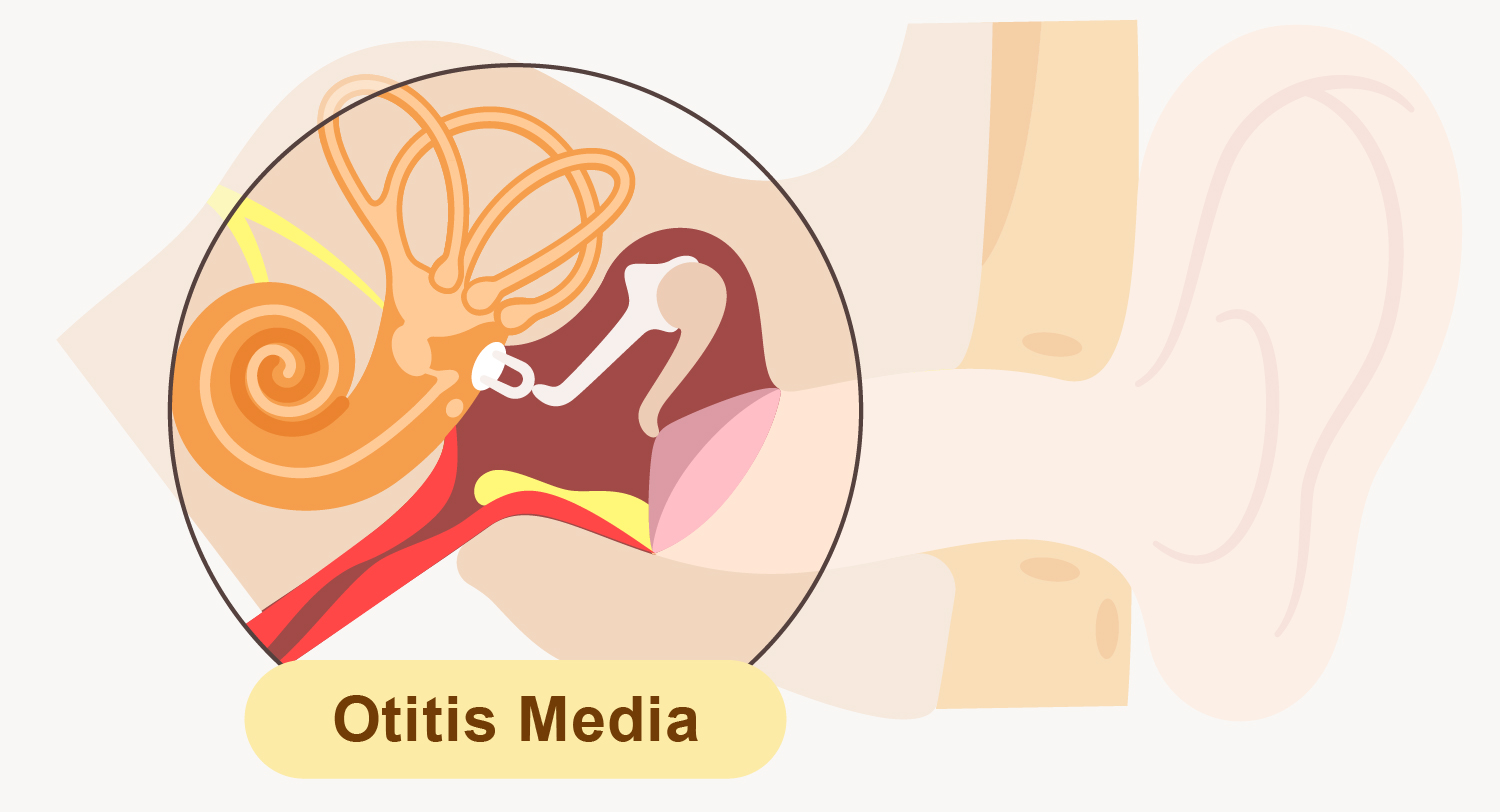
Otitis media is the inflammation or infection of the middle ear where extending from the back of the eardrum to the air-filled space around the auditory ossicles.
The symptoms of otitis media include headache, earache, difficulty hearing, hearing noises in ear such as ringing or buzzing, a feeling of fullness in ear, vertigo, nausea, vomiting, fever and fatigue…etc. For young children, they might show the signs by pulling or rubbing their ears, be grumble, irritable or tired, and unwilling to lie down…etc.
But how does the middle ear being infected? It should start with the anatomy of the Eustachian tube, which is a canal that links the middle ear to the back of the throat. When the respiratory tract is infected, secretion that containing germs would fill up the nasopharynx and block the Eustachian tube. In addition to preventing normal fluid drainage and air pressure regulation in ear, it can also cause the inflammation of the opening to the Eustachian tube. Besides, when the Eustachian tube is severely blocked, the cavity of middle ear will turn into a negative pressure chamber, causing secretion to flow back into middle ear. This condition mostly occurs in children because their Eustachian tubes are shorter than those of adults and are located at a more horizontal position with the nasopharynx, making the blockage worse. Therefore, children are more likely to suffer from otitis media.
When the middle ear is repeatedly infected, secretion would accumulate in the middle ear cavity and cause a condition called otitis media with effusion. If the problem continues to worsen, the consequences could be serious, including complications and sequelae such as cholesteatoma, brain abscess, meningitis, facial paralysis and deafness. Therefore, patients should seek medical attention as soon as possible to avoid delay in receiving treatment.
Treatment Options for Otitis Media and When to See a Specialist
Treatment for otitis media varies depending on the severity of the condition, but it is a similar concept as of treating otitis externa. Mild cases are usually treated with medications to alleviate inflammation and the discomfort caused by the symptoms. For more severe cases, they may require hospitalization for observation and a course of antibiotic treatment. For patients with middle ear with effusion and facial paralysis, surgery may be necessary.
Did you know...
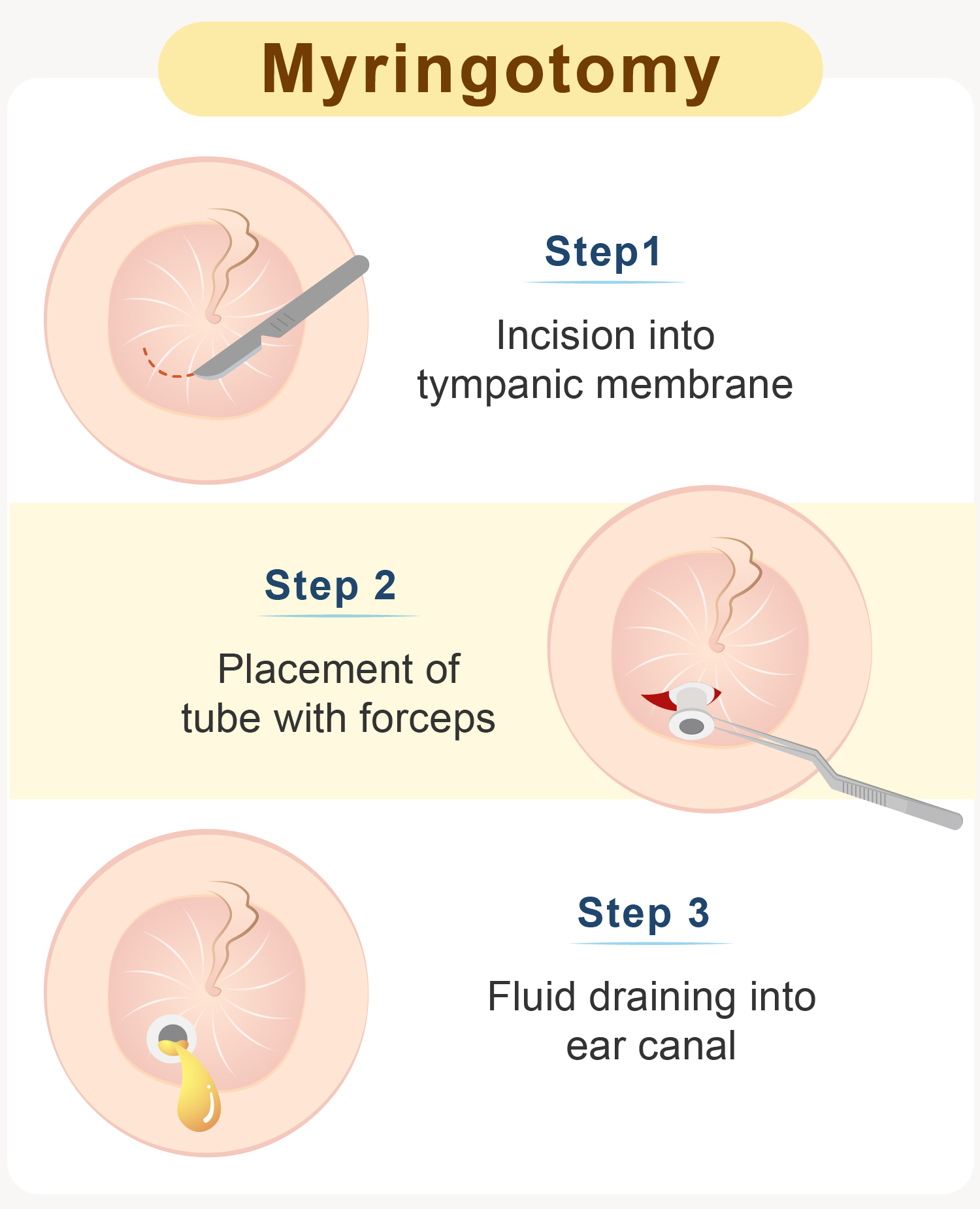
Myringotomy
When the problems of otitis media with effusion or Eustachian tube obstruction become severe (i.e. causing hearing loss), ENT specialist may perform myringotomy to drain the fluid and relief the pressure in middle ear.