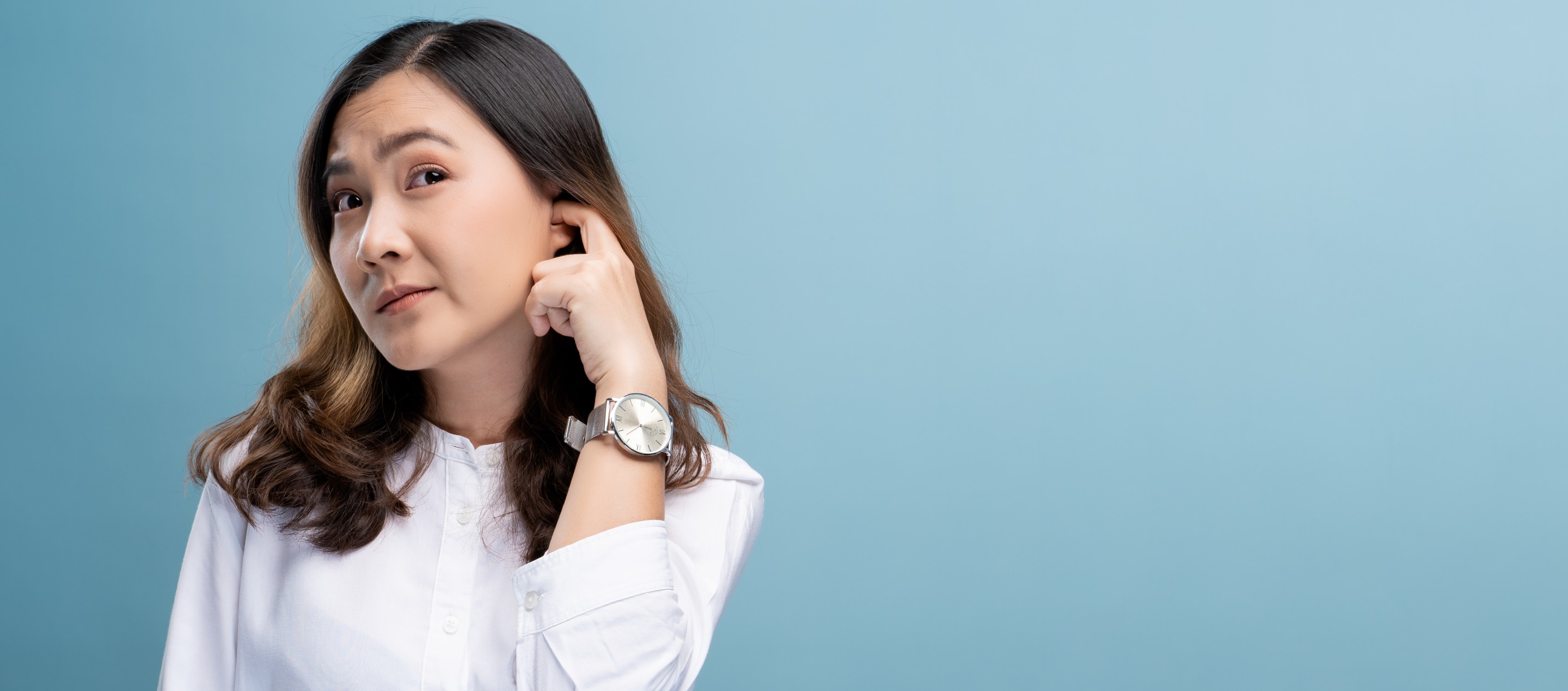
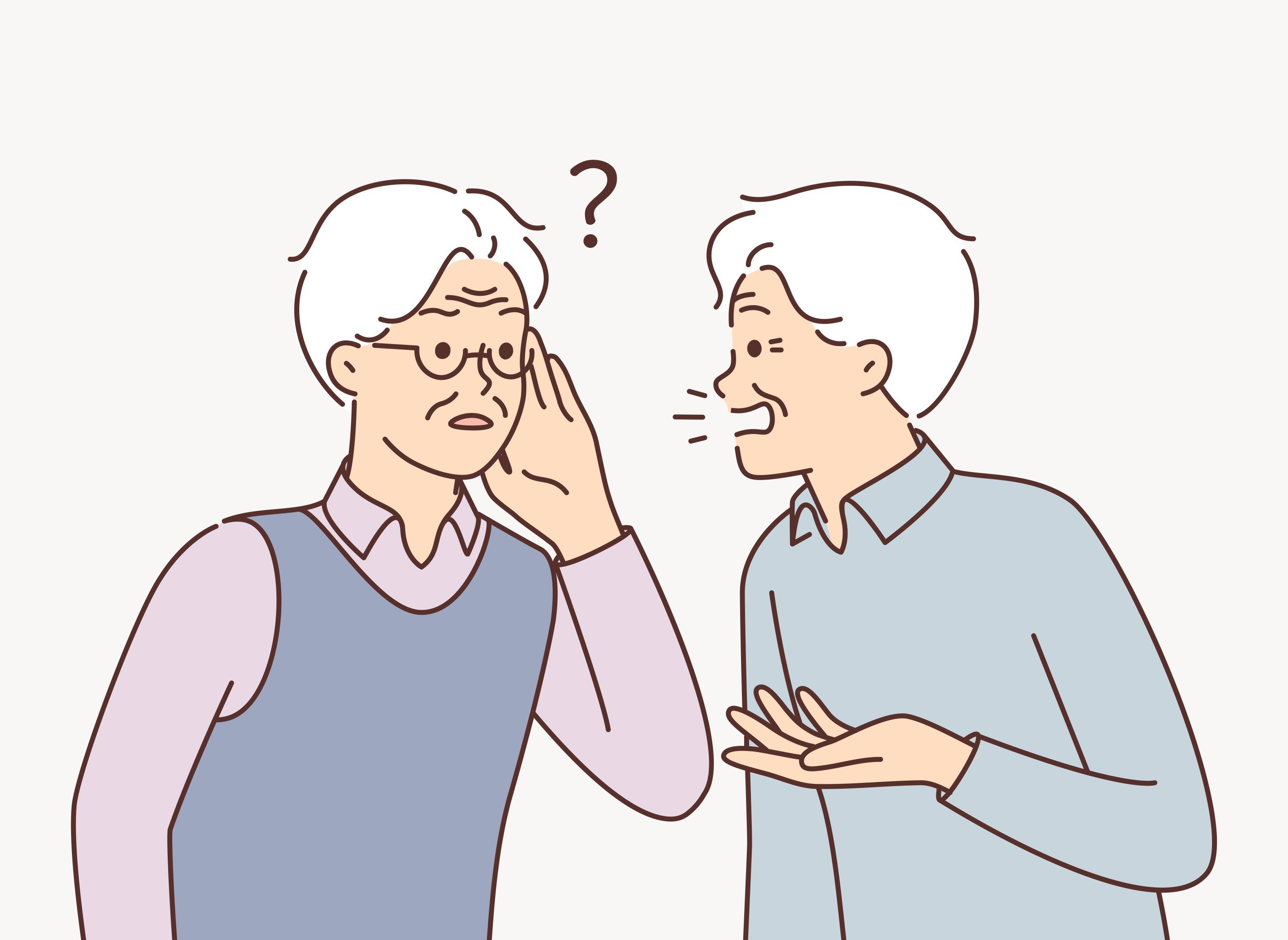
Common Signs and Everyday Situations of Hearing Loss
Perhaps the following situation could be quite familiar to you:
‘In a crowded and noisy train cabin, you heard a melodious telephone ringtone suddenly peals out, followed by a resounding voice of "Hello?" At the same moment, the person on the other end of the line should have begun his/her opening. But then, the resounding voice comes up again, "What? What do you say?" With a voice on the receiver gradually grows louder, a conversation that echoing throughout the cabin begins…'
In fact, having trouble hearing in noisy environments, complaining of others speaking too softly and turning up the phone to the highest volume are the signs of hearing loss.
Types and Causes of Hearing Loss: Conductive, Sensorineural & Mixed
Hearing loss, refers to hearing impairment caused by damage(s) in hearing function, has various causes but mainly can be divided into three categories.
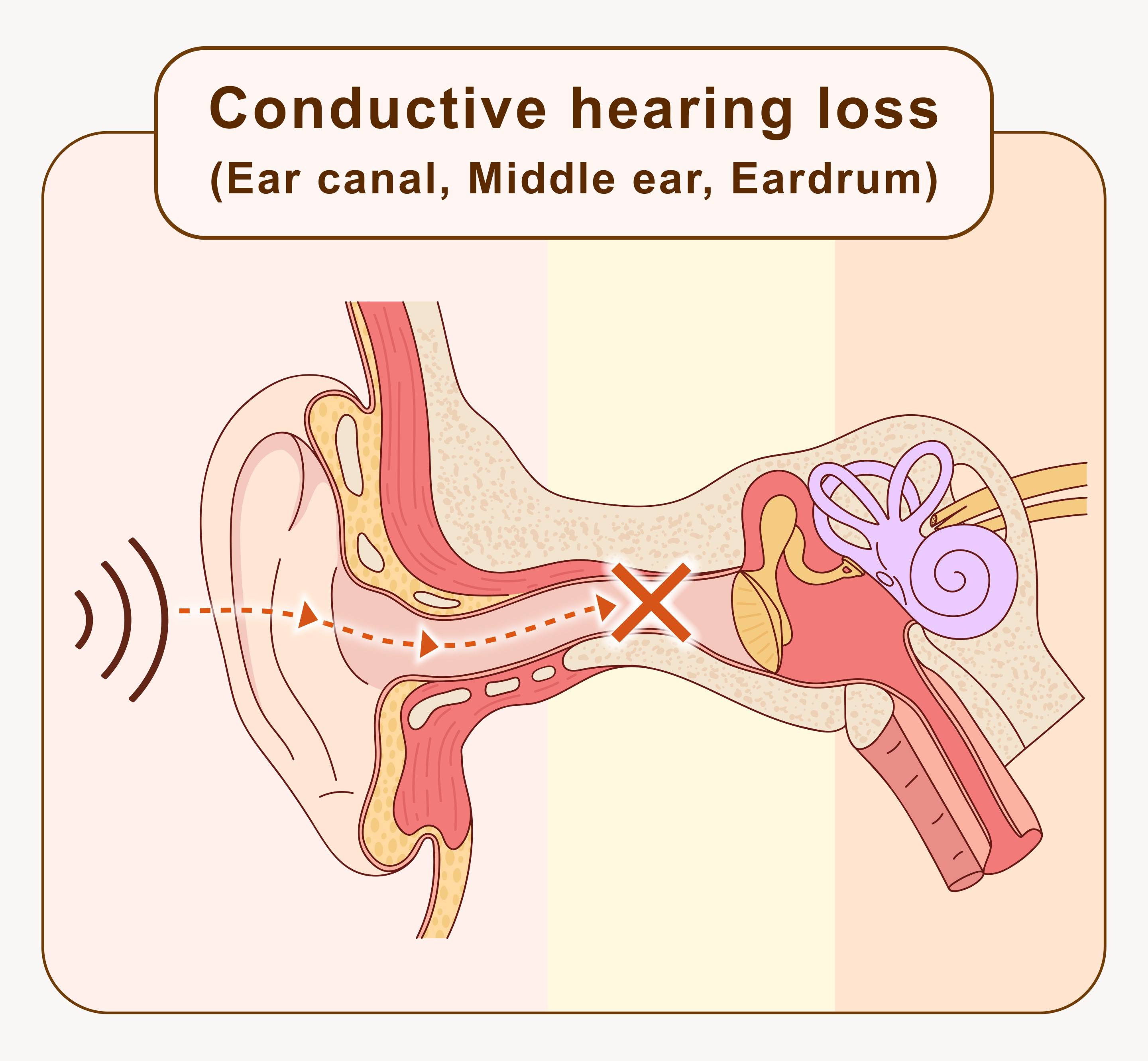
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is blocked during its transmission to the inner ear. Problems may involve the external auditory canal, eardrum or middle ear such as earwax buildup, ear infections etc; it is the most common cause of hearing loss in elderly.
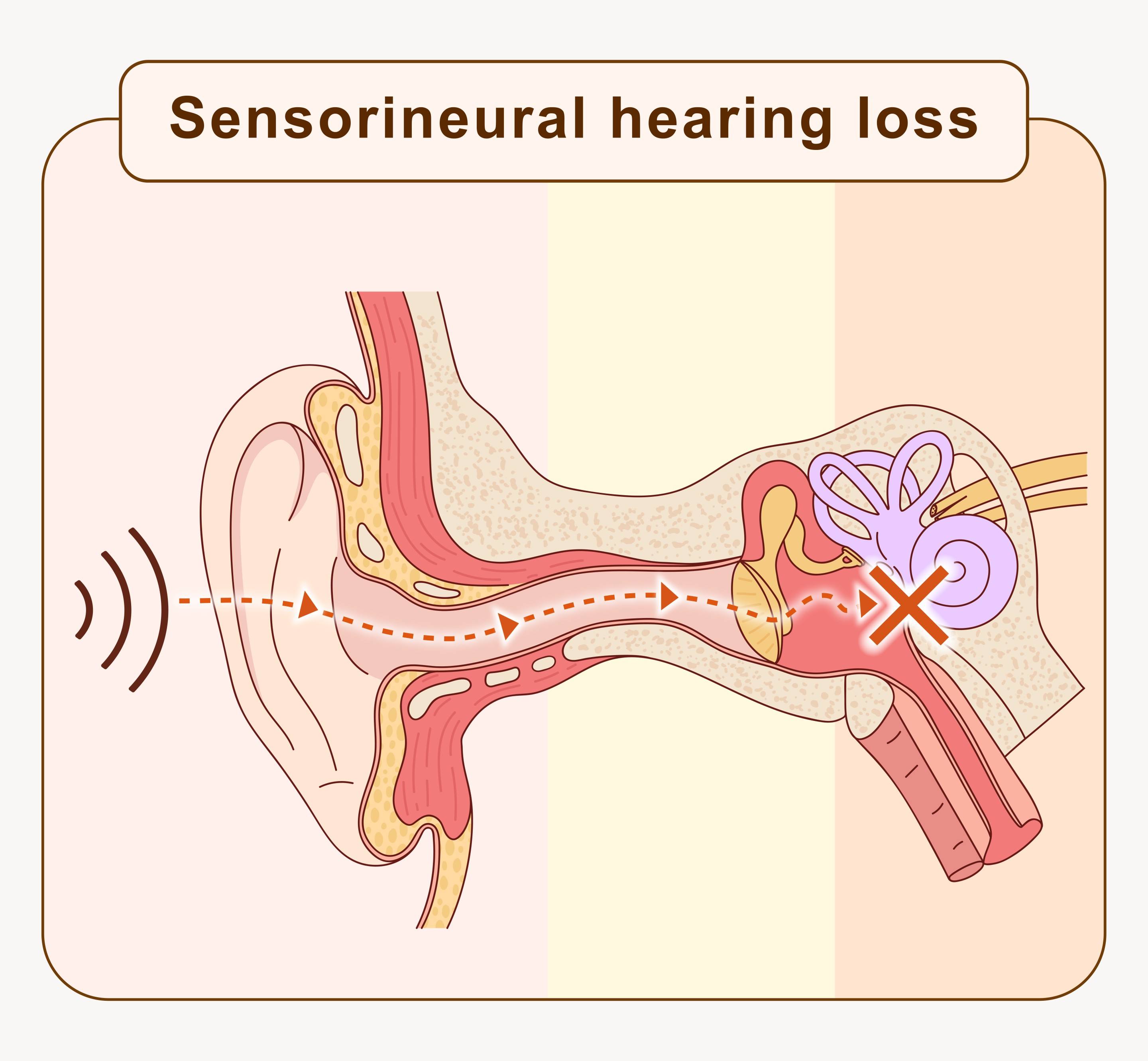
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when sound reaches the inner ear, but the sound waves cannot be converted into nerve impulses (sensory hearing loss); or because nerve impulses cannot be transmitted to the brain (neural hearing loss). Causes may include illness (e.g. sudden deafness), degenerative changes, medications (e.g. the side effects of ototoxic drugs and some cancer treatment medications), noise exposure, or genetics (congenital hearing loss accounts for approximately 0.3%).
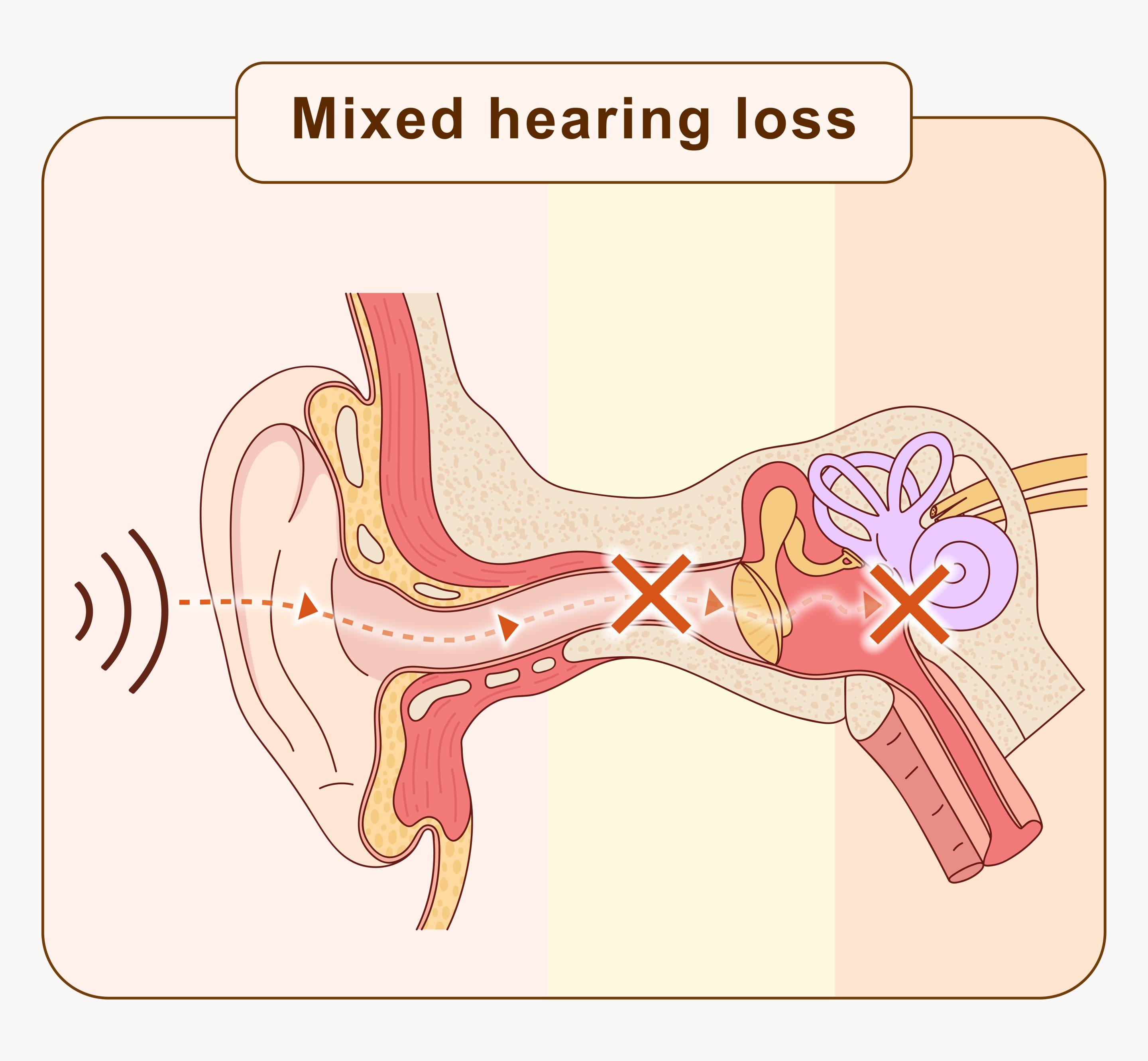
Mixed hearing loss
As the name implies, mixed hearing loss refers to hearing loss that is both conductive and sensorineural. Its causes are complex and require a multifaceted investigation.
The Impact of Hearing Loss on Health and Social Life

Hearing loss not only causes significant difficulties in daily life and hinders communication with others, but also impacts patient's physical and mental health remarkably. For example, due to continuous lack of sensory stimulation, hearing-impaired patient may experience focal brain atrophy in areas linked to sound processing and language, leading to a serious decline in brain function.
Besides, hearing loss can make social interaction difficult too, causing reduction in conversations and avoidance of social situations. Over time, patient may feel lonely and depressed.
Apart from that, hearing loss can also cause embarrassing and frustrating moments for family and friends, for instance:
- Due to the impact of hearing loss, patient may speak louder than others without knowing it, and the voice can easily affect people and surroundings.
- When family member talks to the patient, he/she may not be able to hear the content of the conversation clearly, members may need to repeat the content loudly until he/she can hear; or
- Throughout the conversation, the family member thinks that patient has heard it clearly, but in fact the patient has not heard it at all; when the content of the conversation has been brought to discussion again, it is easy to turn into accusation of "you didn't mention it before" versus "I told you before" .
Hence, the best option for patient with suspecting hearing loss is to consult an ENT specialist as soon as possible to find out the root cause of the problem.
How Hearing Loss is Diagnosed: Medical Examinations and Hearing Tests
In general, ENT specialist would first conduct a series of clinical examinations, including a detailed consultation on the medical history and evaluation of the ear canal and eardrum during patient's first visit. Then, first line treatment, such as medications and clinical procedure (i.e. earwax removal), would be provided in the aim of reducing the impact of hearing loss.
In addition, he will arrange hearing test for patient in need to assess the type and degree of one's hearing loss.
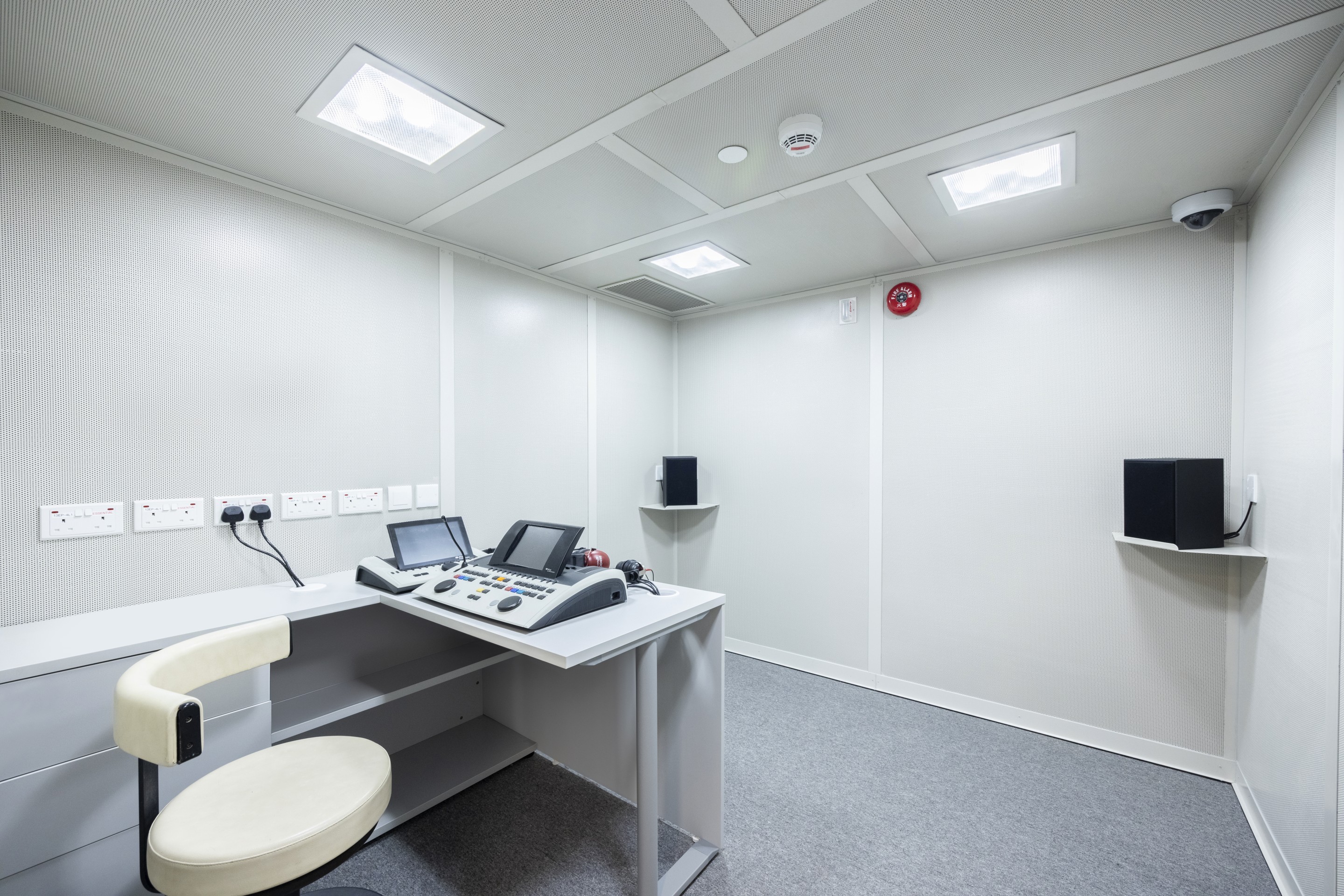

Hearing Test
Hearing test would be conducted in a soundproof room with patient sitting with his/her back to the audiologist and the equipment, wearing a headphone to listen to the audiologist broadcasting tones of different frequencies; at the same time, patient is required to press a button to respond to the sound he/she hears. The test result and report will indicate his/her hearing range at specific frequencies to identify the type of hearing loss.
Normal hearing ranges from approximately 0 to 25dB; a whisper tone is approximately 10dB, while a normal conversation tone is approximately 40dB. Hearing loss is identified when patient can only hear sound levels from 26dB or above; the severity can be classified into five categories, including mild, moderate, moderately-severe, severe and profound.
Patient with mild hearing loss does not recognize any difference in daily life most of the time. He/She may only find difficulties in distinguish certain sound-alike words. However, when situation where patient needs others to repeat the conversation or raise the voice for him/her to hear it clearly, he/she probably has moderate level or above hearing loss.
Once the level of hearing loss is established, ENT specialist will summarize the clinical diagnosis and the results of the hearing test report to provide appropriate treatment or rehabilitation plan options.
Treatment and Rehabilitation Options for Hearing Loss
When hearing loss cannot be alleviated through medication or clinical procedures, doctor will refer patient to audiologist for consultation and fitting of hearing aids, in the aim of enhancing the quality of life by improving one's abilities on hearing and communication.