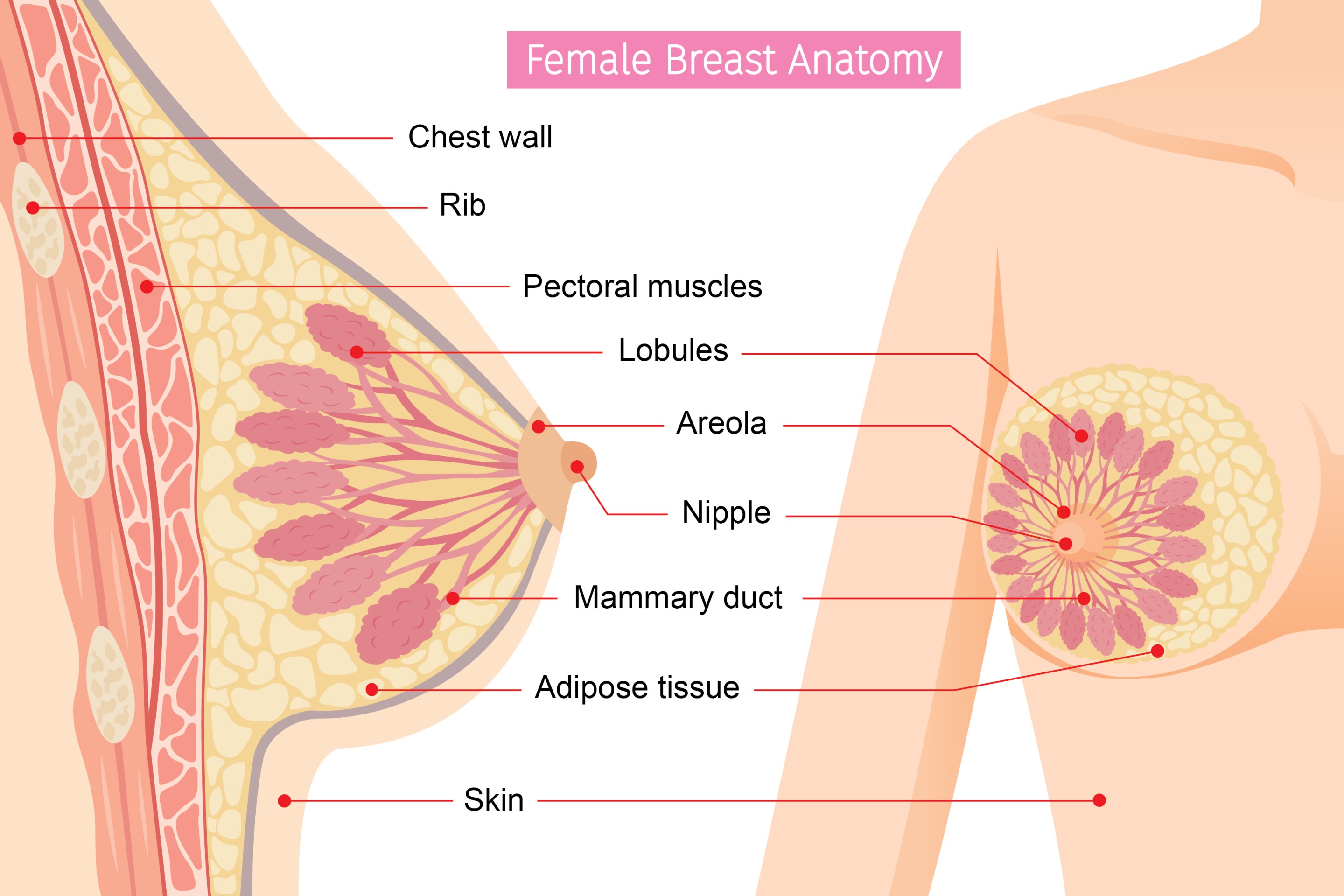
Structure and functions
Breasts are made up of breast tissue and fat, and are held in place between skin and chest muscle by connective tissue.
Breast tissue consists of a complex network of lobules (glandular tissue that produce milk) and mammary ducts (channels that drain milk from the lobules to nipple openings during breastfeeding). Lobules and ducts are arranged in a pattern that looks like bunches of grapes.
The colour of Nipples
Nipples and areolas come in different sizes and colours, from light pink to dark brown. The colour of nipples usually relates to skin colour. It is absolutely normal to have some hairs growing around the nipples.
The skin conditions
The skin tissue of breasts is the same as the skin tissue of the rest of the body. When there is skin condition occurs (such as itchiness, flaking and thickening), patients often concern that it may represent underlying breast cancer. These conditions can be designated into malignant, infectious and inflammatory categories. Patient should seek medical advice early. Clinical examination and sometimes skin biopsy are used to evaluate these conditions.
The difference in breast tenderness between pre-menstrual cycle and others
Breast pain is a common condition. It can be cyclical or non-cyclical. Cyclical breast pain occurs a few days to a week before the menstrual cycle; it could be related to hormonal change. Non-cyclical breast pain does not occur regularly. It can be caused by injury, inflammation or previous breast surgery. Although it is unlikely to identify the exact cause of breast pain, pain is considered to be unrelated to breast cancer.
Is it common to have breast asymmetry?
It is common for breasts to be somewhat different in size. They are sisters, not twins.
Will eating chicken wings increase the risk of getting breast cancer?
There is a saying about eating chicken wings increases breast cancer risk. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this currently. Conversely, high-temperature cooking methods such as deep frying, grilling, or barbecuing until thoroughly cooked have been shown to increase the risk of cancer.
Can wearing underwire bras cause breast cancer?
The answer is "no".
Many women believe that bras, in particular underwire bras, limit lymphatic drainage resulting in the accumulation of toxins in breasts and cause breast cancer. However, there is no evidence to suggest pressure over lymph nodes causes breast cancer. Similarly, going braless does not help reduce breast cancer risk according to current evidence.
There has not been much research on the association between bras and breast cancer because experts always doubted if such connection exists. In one of the studies published in 2014, researchers interviewed over 1000 women with breast cancer and almost 500 who did not have the disease. They found no aspects of wearing a bra were linked to breast cancer risk. These included cup size, number of hours wearing a bra, wearing an underwire bra, or age when women started regularly wearing a bra.
However, there are factors that have been shown to increase the risk of breast cancer - including obesity, smoking, hormonal replacement therapy after menopause, physical inactivity, etc. So, instead of struggling about bra wear, having regular exercise and keeping a normal body weight are more likely to help reduce breast cancer risk.
Likewise, don't forget to perform breast self-examination from time to time. If there is any concern, consult a doctor and arrange a scan in order to detect and treat early disease.
How many diagnostic imaging tests are available for breasts screening? What are they?
There are two screening breast imaging tests to identify breast cancer at early stage when it is more curable; this includes mammogram and breast ultrasound.
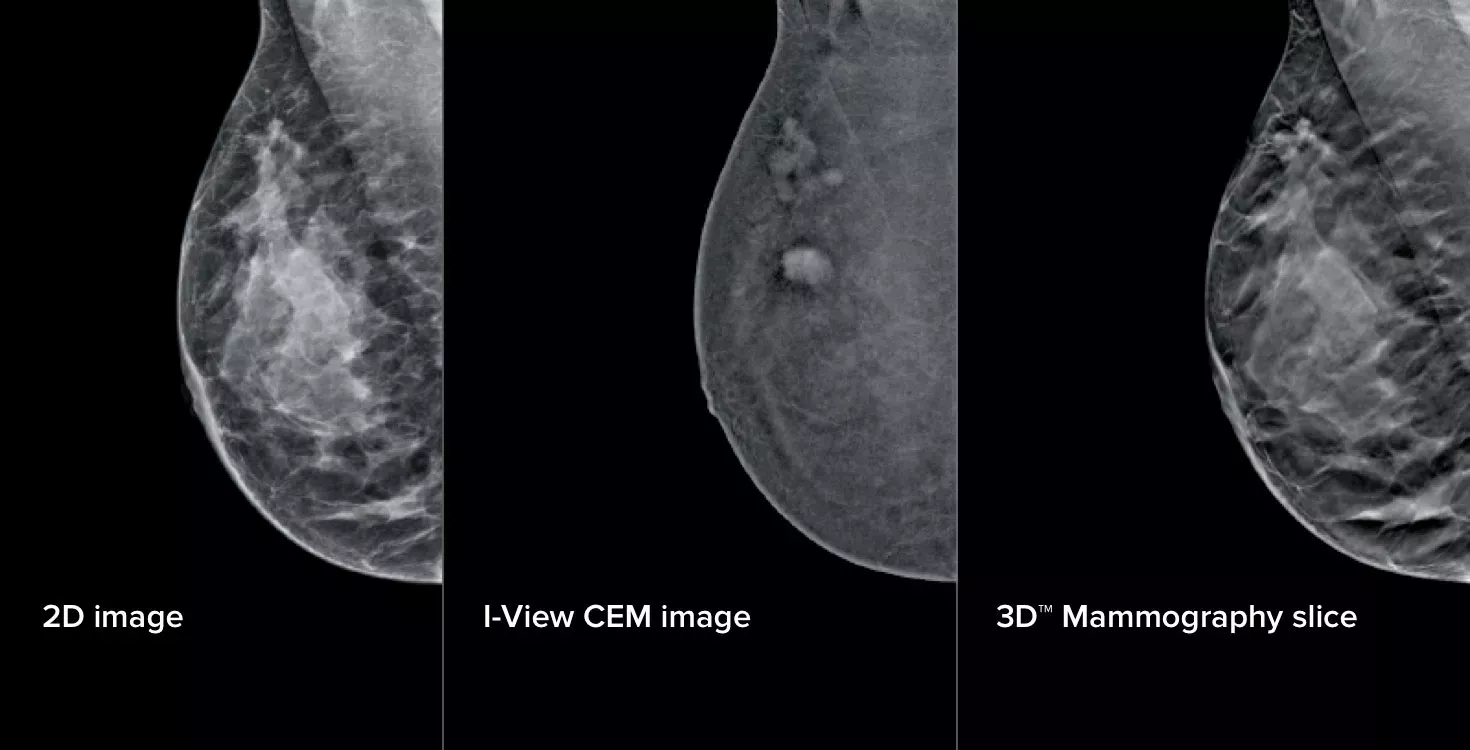
Mammogram is a low-dose X-ray exam of breast tissue. During a mammogram, your breast is placed onto the X-ray machine. It will be compressed while the X-rays are taken. Breast compression is necessary for a mammogram to hold your breast still and minimize movement, which can affect image quality. Compression also evens out the shape of your breast so that the X-rays can travel through a shorter path. This allows for a lower radiation dose and improves the image quality. Screening mammogram is recommended for women at the age of 40 and above.
Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) is an advanced imaging technique that combines traditional mammography with the use of a contrast agent to provide functional diagnostic information. This method enhances the detection of abnormal lesions, particularly in dense breast tissue, by highlighting areas with increased vascularity, which may indicate breast cancer. CEM provides a comprehensive view, assisting doctors in making accurate diagnoses and facilitating timely treatment.
Tomosynthesis, also known as 3D mammogram, uses X-ray to create a three-dimensional imaging of the breast. It has been shown to increase breast cancer detection as compared to traditional 2D mammogram. In addition, it is more comfortable as it places less pressure on breast.
Breast ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce two-dimensional image of breast tissue. In the past, ultrasound was not considered as a breast screening tool. But as dense breast is common among Hong Kong women, ultrasound should be considered as an additional screening option. When mammogram and breast ultrasound are used together, we can have a comprehensive assessment of breast tissue.
( ![]() Click the image to enlarge ) Image comparison between 2D,3D Mammo & CEM
Click the image to enlarge ) Image comparison between 2D,3D Mammo & CEM
Image Source: Hologic, Inc.
> If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to schedule a consultation appointment with our surgeons.
Reference :
Chen, L., Malone, K. E., & Li, C. I. (2014). Bra Wearing Not Associated with Breast Cancer Risk: A Population-Based Case–Control Study. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention, 23(10), 2181–2185. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.epi-14-0414